描述
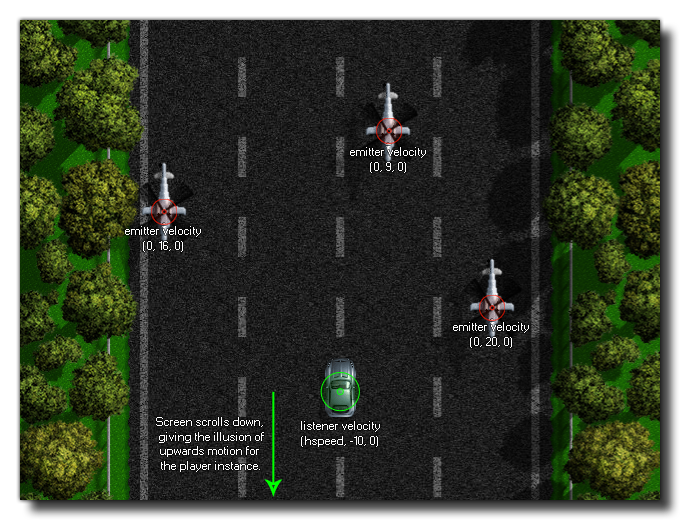
This function can be used to give the listener doppler effects and simulate audio motion based on the vector that is resolved from the given relative x, y and z positions. If the listener itself is not ever going to move, or the movement is not a constant motion, you would normally not need to set these values, but, for example, if you are making a scrolling game where the player has a constant bottom to top movement and the enemies a constant top to bottom movement, you would set the listener and emitter velocities (for emitters you would use audio_emitter_velocity) to the appropriate vectors to simulate the correct doppler effect as they move past the player instance.
NOTE: if you have multiple listeners you should use the function audio_listener_set_velocity.The image below shows how this could be setup for the example game given above:
语法:
audio_listener_velocity(vx, vy, vz);
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| x | The x velocity component of the listener (default 0). |
| y | The y velocity component of the listener (default 0). |
| z | The z velocity component of the listener (default 0). |
返回:
N/A(无返回值)
例如:
if speed > 0
{
audio_listener_velocity(abs(hspeed), abs(vspeed), 0);
}
The above code checks to see if the player instance speed is over 0 and if it is it then uses the appropriate absolute hspeed and vspeed components to set the listener velocity.